The complex relationship between computer hardware and software.
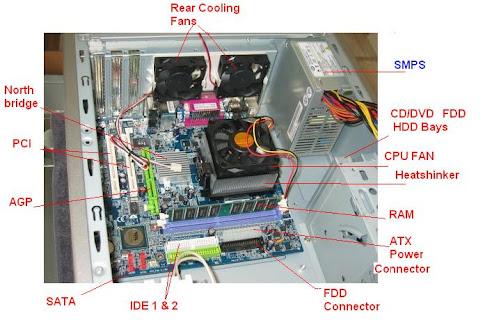
The complex relationship between computer hardware and software. HARDWARE: Physical Components are called Hardware. The hardware includes all of the circuits, drives, expansion boards etc.
BIOS: BIOS is a set of small programs that are designed to operate major PC subsystem. The BIOS runs a power-on self-test (POST) program each time the PC is initialized. POST checks the major subsystems before attempting to load an operating system.
OPERATING SYSTEM: The operating system serves two very important functions in the modern PC. First, an OS interacts with, and provides an extension to the BIOS. This is high-level file handling and disk-control functions. It is this large number of disk-related functions. Second, an OS forms an “environment” (or shell) through which applications can be executed, and provides a user interface.
APPLICATIONS: A computer is to execute applications. An OS loads and allows the user to launch the desired application(s). As the application requires system resources during run-time.